I am starting this journey. Here I will share my notes.
The Culture of the Anthropocene
Anthropocene: it is human activity that is now pushing the planet to the sixth mass extinction.
As emissions increase, we continue to destroy the essential sinks that counteract these.
The biomass of humans and livestock far surpasses that of wild mammals and birds. Most of this mass we slaughter for food, using 77% of agricultural land to provide 18% of calorie supply.
The immense cost of progress has not come to the benefit of all.
Culture is not your friend.
Culture is the normative values and belief systems that coordinate human activity. Culture determines how we understand ourselves and our place in the world. The culture of the anthropocene creates systems of meaning inherently dualistic.
Culture it both constructed and emergent, visible and invisible.
Let’s develop a way to critically asses our cultural systems and find ways to evolve them beyond anthropocentrism.
Fragile societies, not resilient:
- ethnocentric
- humanist
- rationalist
- even pluralistic
Egocentric conception of the self opposed to interbeing and relational. Greedy, excessive and selfish nature. This is wetiko.
Cartesian dualistic logics must always exclude a devalued other. Who counts as human? Separation from nature in order to exploit it. Legitimized ecocide, imperialism, and slavery. Written rational language of the oppressor over oral traditions.
We categorize things as we try to makes sense of the world. We often become overly focused on keeping those containers separate. We forget we made the categories, and start to think of them as universal, absolute, and predetermined.
Culture is not always evolutionary, there is no neat, tidy progressive narrative pointing to greater refinement, complexity, etc.
Any cultural mode holds implicit understandings of what constitutes Self, including the absence of Self or relationality as Self. Through this lens of Self are moral judgements, truth claims, value determinations, ontological lenses and theoretical models of reality.
The archetypal development trajectory of the dominant anthropocentric culture will continue to recreate the fundamental error of separation of self vrs other and from nature until we hack the dominant conception of Self-Other construct.
There is a rich tradition of counter narratives in epistemologies of the Global South, including social movements and indigenous communities, that share a trans-personal sense of the Self that is in radical relationality to both the human and the more-than-human worlds, the seen and the unseen realms. They share a life-centric approach based on kinship, with the living world; reciprocity, generosity, regeneration, consent, dialogue, and solidarity.
Animism → seeing the world and its constitutive parts as living, relational and dialogic. More and more seen as empirically accurate.
Post-humanism → thinking/feeling beyond human gaze, care and concern. It centers life in all forms.
Buen vivir → the subject of wellbeing is not the individual, but the individual in the social context of their community and in a unique environmental situation.
Ubuntu → I am who I am through you.
Interbeing goes beyond interdependence into a radical re-definition of Self through Other.
Part of the cultural evolutionary process requires an understanding of the deep logic, narratives, cultural codes and belief systems of the dominant system; researching and synthesizing life-centric alternatives, especially those rooted in Earth-centric, symbiotic cultures, and testing and iterating new/emerging/ancient narratives in realtime, to expose, disrupt and shift cultural assumptions to create new/ancient/emerging narrative spaces for possibility, transformation and justice.
Genealogical processes of cultural systems:
- language
- speech
- representation
- self-identity
- myth
- belief system
- cultural identity
The creation of Self within the dominant cultural context is the genesis of our conception of history. Things are born, they subsist, and then die; all phenomena that this Self experiences are imprinted with this metaphysical form of space, time and causality.
Narratives are the principal manifestation of culture.
What we believe to be our reality is that subconscious interpretation of the sensations of our body through our own narrative frames.
Culture hack methodology
- Assumption 1: we can gain deeper insight into human behavior by analyzing the narratives that drive them.
- Assumption 2: through the intentional and deliberate reframing of these narratives, we can bring about changes in our belief systems and actions.
- Assumption 3: to dismantle systems of inequality and oppression, we need to change narratives.
Narratives are interpretative social structures that frame our experience and function to bring meaning to everyday reality, guiding our actions and decisions.
If we are not aware of the multiple layers that make up narrative forms, we are blind to what is driving our thoughts, beliefs and behaviors.
Narrative forms are complex, adaptive, evolutionary, living systems. They drive how we collectively make sense of our reality.
Narrative spaces are models of the relationships between narrative forms within a timeframe.
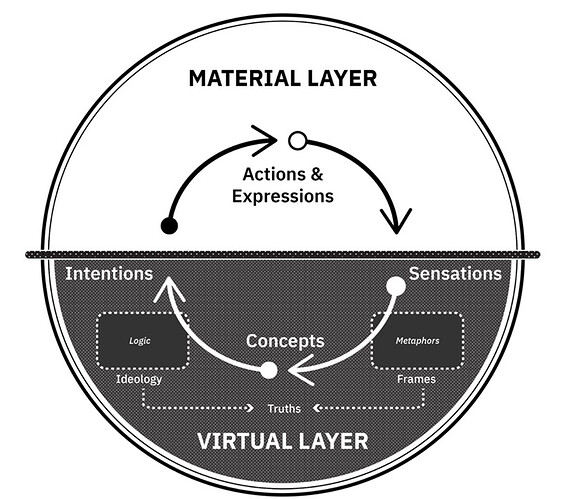
Narrative form principles
- A material layer that is clearly visible and measurable. Most often narrative analysts look for evidence in media. Also collect data through ethnographic methods.
- Virtual layers that are not visible or measurable and influence the material layer. All material expressions of a narrative form are the result of a virtual cultural process. It is not always easy to decipher how they are connected.
- Genealogies, through cycles that move between material and virtual. The layers are interconnected, interdependent, and mutually support each other.
- Emergent, complex, and in flux. A social assemblage. Cannot be reduced to any single set factors.
The material layer consists of a actions and expression, from the narrative form itself and from other narrative forms within the space.
The virtual layer is a transcription of everything happening in the material layer into cognition:
- sensation: first use 5 senses to transcribe non-representational data, like light, heat, sound, into understandable bits of information or symbols.
- conception: second, these perceptions are placed within a structure of meaning, concepts.
- intention: finally, concepts are placed in broader structures of meaning related to self and social awareness. Intentions emerge guiding decisions and actions.
Narrative form sensation happens through multiple human bodies in connected networks.
Narratives allow for collective sense making.
Frames: subconscious narrative structures to immediately make sense of the world. More than linguistic. They integrate all the other levels of the narrative form into one coherent view.
By clearly defining and understanding dominant frames we can understand the larger semantic structure.
Metaphors: the basis of the frames we use. We often do not question primary metaphors.
Ideological constructs: multiple frames into larger structured relationships, coordinated through a system of justification.
Truth constructs: representation of the core beliefs that bind the narrative form together.
These parts are deeply interwoven and entangled.
The way we understand the world determines how we act in the world.
Cultural evolution
The development and transmission of symbolic thought, values, norms and ethical imperatives among humans shape their behavior and impact their evolutionary trajectory. Inheritance of genotypes and symbotypes or cultural traits have led tho the emergence of new forms of cooperation and coordination.
Post-anthropocentric: criticizing species hierarchy and decentering the human.
Progress is against life and against people.
The humanist ideology rejected the deities of our collective animist mythologies in favor of a new system of pragmatism, individualism and self-determinacy; that instills a set of mental, discursive and spiritual values. These values emphasize human agency, freedom and a misplaced notion of absolute morality, and became the emblem of colonial and imperial force, rooted in the demotion of the other. Man is defined in what he is not: female, black, poor, heretic, etc.
This was reinforced by the enlightenment, and has become the dominant force behind progress. This cultural code frames the world as merely a resource for human endeavor, wetiko, a mind virus of consumption, blind to the interdependence and contingency of human life.
Narrative environments
Habitats in which a certain species of narrative forms may live and flourish. Narratives are the very substance of our social reality.
-
Disciplinary: high degree of coherence and low empathy field. The means by which state gains power over society through enclosure. The factory, hospital, school, and asylum.
-
Control: modulated freedom that gives the illusion of liberty.
-
Dialogic: deep diversity and cultural resilience, many heterogeneous viewpoints, people strive to find shared values.
-
Communitarian: high levels of coherence and interdependence. Local resilient communities that work together to preserve life and thrive together.
Narrative environments with high level of resilience ideally move between dialogic and communitarian as needed.
All these are anthropocentric and are contributing to a breakdown of the systems that sustain life.
The current movement of transition requires understanding the world as entangled and animistic, as mutually caused. We see nature as something we are, not as something to save.
- Interbeing: post-anthropocentric and pre-dualistic (before any conception of separation). Similar to panarchic, diversity+homogeneity. One of the characteristics of syntropic systems.
Onto-shift: a fundamental shift in how we view and understand the world. The new ontology is non-anthropocentric, a life-centric way of being.
Systems entropy: lack of order or predictability, gradual decline and chaos.
Systems syntropy: energy concentration, order, organization and life.
Cultural evolution is the shift from entropic to syntropic narrative environments through a widening definition of identity, an animistic and quantum wiew of Self.
Do you want to be or interbe?
Culture hack method
- Ask the correct questions to develop a point of view.
- Listen to the narrative space.
- Understand the key insights of the narrative forms.
- Reframe the deep logics, beliefs and assumptions.
- Hack the narratives we want to shift.
Our ultimate goal is to change the dominant culture and shift the beliefs that create, sustain, and perpetuate the Anthropocene.
1. Ask
Collectively ask the correct questions to develop a point of view statement. A statement that outlines the context and goals of the narrative intervention you want to engage in.
Bring together the stakeholders of the narrative intervention in a collective exercise to more deeply understand them. We are not erasing individual narratives, we must find the unifying thread and find the commonality that shows how interconnected we are. Create a sufficient common identity that people are willing to join.
Guides
- only together we all know everything.
- people are experts in their lives. Local knowledge is legitimate.
- the problem is the problem. The person or community is never the problem. The problems to which we respond have their origin in structural inequality.
- we are not neutral. We want to contribute to stories that recognize the dignity of people and communities.
- identity is a collective achievement.
- identities are multi-historian.
- document knowledge to transcend the moment.
- create links to help enable the worlds we want to see.
Questions
- who are you? with emphasis on the project team and the stakeholders. Skills, capacities, geographic location, demographics… In what way will this impact the stakeholders?
- what is the motivation? why is is important to you as a collective? what facts determine the scope?
- what is the desired outcome? what can be the impact of the intervention? what does success look like?
- how will you create the change you desire? List of actions in light of the common goal.
- how can we represent the different voices?
Take your time because it will be your compass and guide.
2. Listening
Explore the relationships of the interlocked parts of a narrative, such as the spaces, actors, actions, momentum, and sentiment of a conversation.
Construct a listening model to set the parameters for our inquiry.
Small listening: interviews and surveys, manual collections on websites and social media platforms. Identify nuances and texture in narratives, especially if we want to investigate the broader patterns we find in the big listening.
Big listening: use software to observe and collect data online, in the communities and outlets that propagate a narrative. Making relationships in online networks visible and usable for our work. Identifies the broader patterns to identify themes and points of intervention.
A listening model is unique to an inquiry, oriented to the analysis of complex systems.
We locate:
- nodes: the basic units of narrative communities. People, publications, groups, businesses.
- narrative communities: social networks involved in an active discussion about a topic or issue.
- echo chambers: narrative communities which primarily talk amongst themselves and are insular.
- power dynamics and structures: show which narrative forms are dominant and which are emergent.
Pay attention to: demographics, themes, platforms ,date range (preferably in the present), geography, strategy (how will you collect data).
Be as specific as possible.
What events have shaped or mobilized public opinion? Who has been influential? Is your topic related to mainstream topics? If there is no actual conversation about your topic, what is a broader or related space you can listen to?
Coding your data is an interpretative process. Words or short phrases that label data based on the patterns you find.
- deductive: assign codes before retrieving the data.
- inductive: create codes once data is collected and patterns start to emerge.
Keep your point of view, concerns, and goals to guide coding.
What are the key questions you want to ask the data?
What are the overall trends and patterns? Who and what are the most influential? What are they saying? Do they interact? What are we not seeing in the data?
3. Understanding the narrative space
Culture hacking is only for self-defense.
Narrative communities are dynamic and in movement. Be sensitive to understand the right moment to conduct a hack.
Narrative communities are groups of people talking to each other persistently about a specific thing over time. Map these communities and their underlying belief systems to inform our narrative strategy.
We can identify their justifications for action and guide our narrative intervention.
Identifying narrative communities
You will see narrative communities emerging from your data insights.
Name your narrative communities and provide a brief description. Analyze how they organize themselves and the potential they have to evolve the narrative space.
- nodes are talking to each other in an ongoing conversation.
- the conversation is about shared topics and events.
- actors have a shared perspective, belief system and ideology.
- they often have a shared geography.
- the language, concepts and terminology is shared.
- these communities are defined by the distance between them in the network which measures their level of interaction.
Cluster nodes by language, time, and power.
Analyzing narrative communities
- Attention: find the narrative communities that are bigger and have more interaction than others. Understand key features, themes and volume of activity. Show the most important events in the timeframe.
- Network: relationships between actors. How communities are related. Understand the virtual layer by their semantic and semiotic content.
- Power: map the political system by identifying dominant and less powerful narrative communities. Narrative communities that have the most attention and network interactions over time have the most power.
Creating maps is a political process in which we are enacting our worldviews, politics and belief systems.
Mapping narrative communities
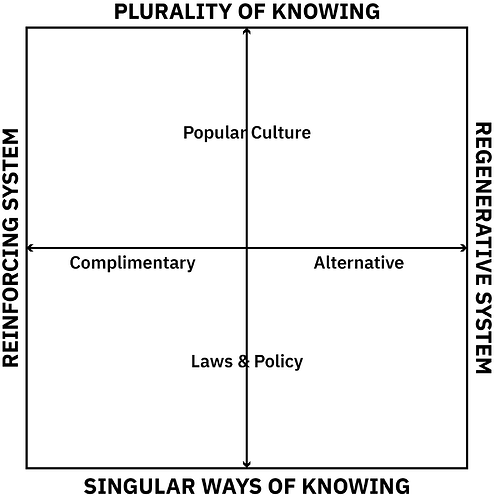
System-knowledge framework. Mapping between ways of knowing and modes of being. Heterogeneous groups that are defined by their interaction with information and their relation to systems of oppression.
The system spectrum:
- communities that with their narratives and actions reinforce the current systems of domination.
- communities that are complimentary, akin to these systems of domination but do not completely reproduce them.
- communities that present alternatives to the systems of oppression.
- regenerative life affirming systems. Live-centric and actively dismantle systems of oppression.
The knowledge spectrum:
- a belief that there is one truth in the world.
- laws and policies, aims for incremental changes.
- popular culture, reproduce popular knowledge, not specialized but not heterogeneous.
- plurality of knowing in the service of life. Allowing diversity to flourish.
Identifying and analyzing frames
Frames are mental models that we use to interpret the world they serve as mental structures for unifying ideas and concepts made up of a mix of facts, experiences, emotions, memories, and assumptions.
We have frames for words, people and objects.
- what is inside the frame?
- what is outside the frame?
- how is what’s inside constructed?
what’s absent in the discourse often says more than what’s present, to elucidate metaphors, logics and power.
Linguistic analysis:
- verbs: what action is being represented? static, dynamic, fast, slow, serious, playful.
- hidden assumptions: what is represented as positive and negative? how can we tell? adjectives.
- imagery and metaphor: what images does the language conjure in mind?
- subjects and objects: who is active and who is passive? who is going the work? who has the power?
- power: is this conversation in a growing phase? does it exist and endure overtime? does it allow diversity? are nodes consistently engaged?
Identify metaphors and logics related to recurrent frames. Identify the overall power presence and potential for evolution.
Articulate your narrative objectives
What do you want to shift in this narrative related to your point of view?
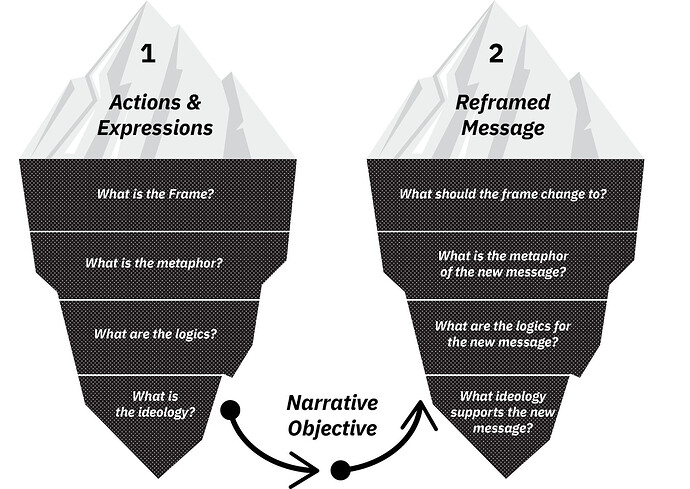
4. Reframing narratives
Changing the frames you identified to new ones that can support the objectives outlined in your point of view statement.
The assumption is that we can change the current narrative frames around a particular topic to activate new logics, new ideas, truths and beliefs.
Make the virtual layer perceptible and change it to better reflect the beliefs and ideas we seek to promote. Question the cultural narratives we take for granted.
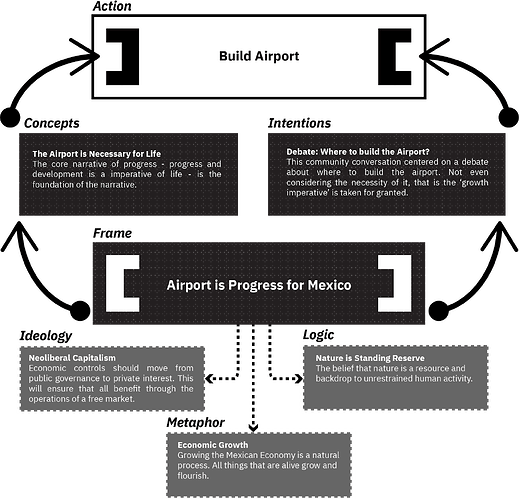
Example: in México there was a project to build an airport in a lake.
Analyze
- Metaphor: what are the metaphors embedded in this narrative frame? What sensations does the metaphor evoke in your body?
The airport is progress, progress is growth, evokes a sense of natural growth, life. - Logics: our belief system and the truths we assume and do not question. What are the truths and logics embedded in this narrative frame? What do you need to hld as true in order to believe this frame?
Nature is a commodity, only then can you agree to destroying an ecosystem to build the airport. - Ideology: the cultural context and the justification for action held by society. What is the ideological foundation of this frame? What cultural context is justifying this frame?
Neoliberalism.
Change
- Metaphor: think of other metaphors that can reflect your narrative objectives. Which metaphor helps you move the narrative towards a life centric and syntropic fame? Which metaphor help you speak to and unite the communities you are targeting? What metaphors can create a paradigm shift?
Think of the lake as a living being. - Logic: what kind of belief systems do you wish to underpin? What underlying assumptions are you trying to communicate? What are the most radical truth constructs that the communities are willing to accept?
Animistic view, all beings and things are alive. Nature is alive and sentient. For me to exist, the lake must exist. - Ideology: what ideology can you utilize to justify your metaphor and truth constructs? What ideologies are latent that you can bring to the fore? What evocative belief systems and philosophies can you use?
Rights of nature for the lake.
Create a new frame
We advise to come up with several frames. Be intuitive, tap into your knowledge and instinct. Keep your mind in your point of view and your narrative objectives. Adopt a forward thinking mindset.
What kind of ideas, intentions, actions, behaviours, and material expressions could be unlocked?
Remove focus from the airport, laid emphasis on the community and on the interdependence of humans and nature and the possibility to choose life.
Why?
To evolve narratives beyond anthropocentrism, and towarts an ethic of interbeing. Unity and harmonization through underlying logics so we are more likely to convince the critical mass of the public needed to shift culture in the direction of life-affirming futures.
Overton window or window of discourse: range of political ideas deemed acceptable. Make the radical common sense, move the overton window towards the non-anthropocentric cultures based on an ethic of interbeing.
The narrative strategy
Change the trajectory of a narrative to trigger new actions and events.
- Which narrative communities are you focusing on?
- How will you engage them to achieve your narrative objectives?
- What medium will the intervention be?
- What is the current trajectory of the various narrative communities?
- In what way do the narrative communities intersect?
- What direction do we want these narrative communities to take?
- What kind of intentions and actions do we seek to encourage?
We must decide who to speak to and who is best positioned to spread the message. Age, gender, tastes, political-stances, socio-economic situations.
- What are the shared interests?
- Is there a common discourse? a recurrent theme?
- Is there a preferred type of media?
- What are common metaphors, myths, symbols?
- Who are the leaders and influencers? What is their difference?
What the hack?
Create a viral message that can spread and shape the narrative space.
Message
The translation of your new frame into words.
Messages are the actual manifestation of narrative frames in the material world. Language is a key building block. Choice of words matters, it enables us to highlight certain things and hide others.
Take into account adjectives and nouns, subjects and objects, passive or active voice, verbs.
Draw focus to what you believe is most important. Consider your target audience. Try and test your message.
Meme
The condensation of that message into a simple cultural unit that can jump quickly from mind to mind.
Has the potential to go viral. It will most likely use an existing symbol. Try to use or replace them. Symbols evoke and represent reality. Metaphors can be useful in finding new symbols.
Be nimble, specific, and minimalist.
Tone
Emotions that are evoked through your message and that you are spreading in the conversation.
Understand and analyze the sentiments of a public conversation, this gives us an indication of where we can intervene. Pay attention to general patterns of emotion that exist over time within the narrative communities, and to temporary emotion reactions to a particular event.
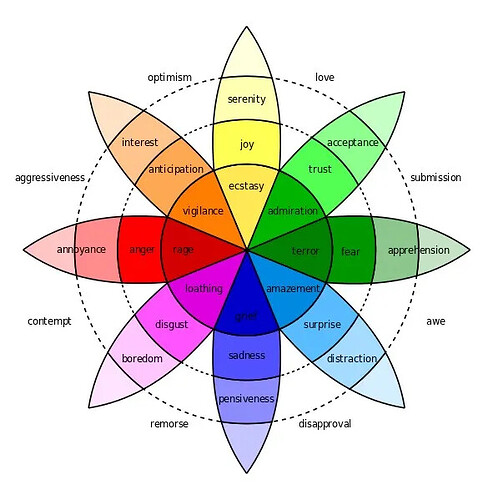
Use plutchik’s wheel of emotion as a starting point. It’s simple and there are nuances not captured.
Bring in creatives and artists who know how to translate emotions into material forms. Handle with care to not retraumatize or victimize.
Media
Best format and platform to reach your target audience.
Appropriate is the one that will achieve the most impact among your audiences. The format most likely to be understood and shared. Find the best formats and designs.
Choose the right moment in time and space
Seed your hack to make the most impact.
Power dynamics exist in private and public spaces. Choosing is a political declaration. Through hacking narratives we can shift the power dynamics.
There are spaces of production, extraction and destruction, consumption, decisional power, symbolic places, of communication, counter-culture, imagination, decentralized and horizontal. Identify security implications.
Choose the scale. Who gets to see the message, how often it is repeated.
Conversations are made of peaks and dips. Identify the moment most likely to get picked up and shared. Monitor conversations to pick.
Iterative cycle
Launching a culture hack involves trials and errors. Develop various actions to test which one lands.
Monitor and evaluate results. Fine tune and re-design to launch again. Identify what you seek to measure.
A/B testing, randomized control trials, focus groups, social media monitoring, surveys.
Life at the center
Is this in service for me, my community, the planet? Is this serving life? Give space to self-criticism and honesty about your individual capacities and needs.
- Self-care: we cannot give what we do not have. Pause and ask if we hold the spiritual, physical and emotional capacity to do the work. Our body and spirit are the first territory we must defend.
- Team up and delegate: remain self-critical and accept when we do not have the ability. Build community.
- Relationships build the world we dream of. Sometimes the simple fact of asking someone to be part of a culture winds up being the change we are seeking.
- Inclusive communication and co-creation of infrastructure build communities. Infrastructures are what hold and contain these narratives.
- Sustainability means defending and protecting life, connect local actions with international and global actions.
- Weave relationships between communities and the home we share.
- Interdependence means we are part of a whole. The individual, the community and the territory. In other cultures there exist other forms of being and existing. The human being and the white male human are not the centre of the universe.
- How we may be complicit in strengthening narratives, infrastructures and actions that perpetuate the anthropocene? Always ask about our blindspots and wonder about other forms of being, thinking and doing.
Foster a culture that doesn’t place value on accumulation, encourages mutual care with planet, propose post-anthropocentric ethics and values. Syntropic interdependent view.