Flashbots x Axelar - SUAVE Bridge Proposal
Hi everyone, I’m representing the Axelar Foundation. We recommend that SUAVE leverages Axelar network’s decentralized infrastructure for cross-chain use-cases.
Situation
In the current implementation of the SUAVE client, Flashbots uses a centralized bridge. Flashbots seeks input and expertise in bridge designs that optimize security, decentralization, chain scalability, and user experience.
Proposed Solution
Replace the existing centralized bridge with Axelar network’s decentralized, proof-of-stake solution to transfer assets for gas and MEV applications.
Security
Security of cross-chain systems has requirements similar to those of blockchain consensus protocols, namely safety and liveness.
- Safety: It must be extremely hard for an attacker to steal funds.
- Liveness: Transactions will always go through within some timeframe.
- Decentralization: This is not necessarily a separate requirement but rather a means towards satisfying the properties of safety and liveness.
Axelar network security is powered by a combination of:
- Proof-of-stake decentralized design at the core.
- Novel quadratic voting mechanism increases the decentralization of the network.
- Validator security policies, such as mandatory key rotations.
- Network functions that enable mitigation of malicious interconnected chains [suspend traffic from them].
- Contract limits that specify how much can be transferred over a time period.
- Docs
- Rigorous audits & bug bounties.
- Code
Uniswap Foundation announced in June of 2023 that Axelar network & Wormhole are approved to support the next phase of its development for cross-chain governance. The foundation has used a group of nine experts to analyze six of the leading crypto bridge providers. After a comprehensive review involving code evaluation and direct interaction with the bridge teams, the committee approved Axelar network & Wormhole for Uniswap’s specific use case of protocol governance. Other bridges, including LayerZero, Celer, DeBridge, and Multichain, did not meet the committee’s criteria.
“The analysis of Axelar concluded that it conditionally satisfies the requirements of the Uniswap DAO’s cross-chain governance use case, as outlined in the Assessment Framework. Axelar employs a proof-of-stake mechanism with sound cryptoeconomic guarantees to secure the protocol. Various aspects of the design of the protocol appear to be well-considered. The size of the validator set and the thresholds for ensuring safety and liveness are sufficient. Its technology stack is built to high standards, and the team maintains good development practices, with strong attention to detail and high activity levels for ongoing improvements. A source of concern for the Committee is a 4-of-8 multisig that governs key aspects of the protocol. Axelar has communicated its plans to move away from reliance on this multisig in Q2 2023 and the committee has weighed in on that process. The Committee recommends that the Uniswap DAO adopt Axelar, conditional on a successful transition away from this multisig. Additionally, the Committee recommends ongoing monitoring of updates to identify areas for improvement in the protocol.” Read more here.
Since then, Axelar network has upgraded to fully decentralized governance. Details of the new Axelar Gateway Governance can be found here. Changes to protocol parameters, including upgrades, now require a quorum of validators to take effect. Axelar network uses the same trust assumptions as message passing for protocol governance changes.
Decentralization
Axelar network is a full-stack decentralized transport layer governed by permissionless PoS consensus. Axelar network is the only “open stack” on the market. All of its components can be upgraded and improved by the community. It provides universal composability of programs with any-to-any cross-chain capability. Users access consolidated pools of liquidity. Developers do not need to speak any custom language; they do not need to make any changes to their chains or UIs.
The Axelar network has three critical components across two functional layers.
- The first is the network itself, composed of validators responsible for maintaining the network and executing transactions. The validators run the cross-chain gateway protocol, a multi-party cryptography overlay on top of a Layer 1 blockchain. They are responsible for performing read-and-write operations to gateway accounts deployed on connected external chains, voting, and attesting to events on those chains.
- The second are the gateways, effectively smart contracts that connect the Axelar network and its interconnected external chains. Validators monitor gateways for incoming transactions, which the validators READ. They then come to a consensus on the validity of that transaction, and once agreed, they WRITE to the destination chain’s gateway to execute the cross-chain transaction. The funds are sent to a generated address on the source chain and are locked, and a corresponding asset is minted on the destination chain. The validators and gateways compose the core infrastructure layer.
- Sitting on top of the validators and gateways are the APIs that enable developers to access the tools and infrastructure enabled by those validators and gateways. This is the application-development layer that applications will interact with to go cross-chain. The underlying core infrastructure layer is used to pass customizable, generalized messages across chains. These APIs are how developers can easily lock, unlock, and transfer assets between any two addresses on any two blockchain platforms, execute cross-chain application triggers, and, more generally, handle any cross-chain requests.
Chain Scalability
Presently, Axelar network connects 54 chains, the highest coverage of all available interoperability solutions.
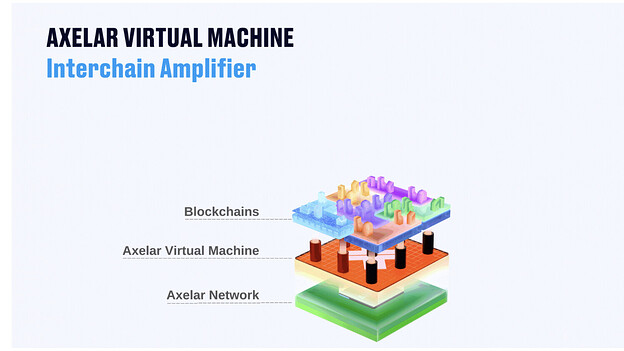
Axelar network’s coverage and scalability of chains is set to grow exponentially with the launch of Axelar Virtual Machine. The Axelar Virtual Machine is a programmable interoperability layer that automates complex multi-chain deployment and management. The Axelar VM helps developers to span the whole of Web3, as if they were building on a single chain. It is powered by Cosmwasm and turns interoperability into a programmable layer.
The Interchain Amplifier enables developers to permissionlessly set up connections to the Axelar network. Developers gain access to Axelar network’s interconnected network of chains and can “amplify” their resources by paying the cost equivalent to developing only one connection. They can establish connections between new ecosystems or existing chains to add new network properties, such as improved security or better delivery and availability.
For example, once Ethereum develops robust light-clients & ZK proofs for its state, a developer can easily integrate them into the Axelar network to replace or enhance an existing connection.
Developers can also leverage independent connectivity paths to enhance security at the application layer. In a blog introducing multi-path routing, it is described how, for lower-value transfers, an application can choose to accept messages authorized by any of the available connections. For higher-value transfers, the application can require messages to travel multiple independent paths, before approval. This architecture, combined with forward-compatible dApp deployments, enables developers to build scalable interchain technologies while adapting to future improvements in the cross-chain networking layer.
User Experience
Most cross-chain user experiences are complex and painful. 1-click user experiences are necessary to onboard billions of users. Unlike alternative solutions on the market, Axelar network is programmable: it’s a blockchain that connects blockchains, providing an innovative contract platform that supports superior UX:
- Tools like Interchain Token Service allow dApps and tokens to function on multiple chains in the same way as they function on their native chains.
- Tools like Axelar Gas Service automate burdensome user tasks like converting into multiple gas tokens to execute a cross-chain transaction.
Cross-chain Intents are live on the Axelar network: Squid, a liquidity router, has used intents on Axelar network to execute cross-chain swaps in seconds. Axelar network can easily work with new cross-chain intent executors. Intents create fluidity between off-chain and on-chain worlds by allowing third parties to fulfill users’ desired actions efficiently. Intents improve interop UX by settling actions almost instantly and then safely finalizing them later.
On the Axelar network, intents have been seamlessly operational. They are exceptionally efficient for transactions that tie value to a specific token, enabling swift order fulfillment. They can also be expanded to more generic messages as long as developers can define their intent structures meticulously. If the value of an intent can be quantified, then solvers can price the risk of it failing to finalize. The risk to the solver of executing a solution to a complex set of user intents between many chains could be aggregated into a single fee, allowing them to execute simultaneously but finalize separately. A small fee to the solver is vastly offset by the improvement in usability and efficiency for the user. We like the work that Essential is currently doing with the concept of “Intent Standards."
One notable Axelar ecosystem application, Squid, has successfully employed intents on Axelar network by integrating with the GMP Express interface. The result? Instant cross-chain communication.
Squid is a cross-chain liquidity router built using Axelar GMP. The dApp finds liquidity in DEXs on connected chains so users can initiate swaps with a single click. The user experience (UX) mimics what users expect when transacting between different chains’ tokens on centralized exchanges – except the entire transaction runs on decentralized infrastructure.
However, there is one aspect in which Squid cannot duplicate a centralized order book using exclusively on-chain infrastructure: as discussed above, finality on connected chains can take 10 to 15 minutes. Instead of making the user wait, risking slippage, Squid employs intents in a fast-finality gadget called Boost. Squid Boost completes the action described hypothetically above in real transactions. It serves a user’s intent to swap X for Y between chains A and B. Boost completes the intent on B, then recoups funds when the transaction finalizes, absorbing bridge risk and delay. Here’s an example transaction.
Conclusion
Axelar network’s architecture meets Flashbots’ requirements on Security, Decentralization, Chain Scalability, and User Experience. We believe Axelar network’s cross-chain infrastructure presents the right solution for SUAVE Bridge.