My highlights: https://ia601600.us.archive.org/35/items/elopio-papers/2023-measuring_the_concentration_of_control.pdf
Ethereum is undergoing significant changes to its architecture as it evolves. These changes represent an evolution toward a more modular architecture, in which there exists new exogenous vectors for centralization. This paper builds on previous studies of decentralization of Ethereum to reflect these recent significant changes, and Ethereum’s new modular paradigm.
Propose a model for measuring decentralization that accommodates structural changes in wider network topology over time.
A model that views Ethereum as a socio-technological ecosystem in which significant components of the network develop outside the core protocol.
- The size of the infrastructure compared to the base layer
- The potential effect on the base layer should the infrastructure be compromised or develop misaligned incentives
Account for the changing topology of the ecosystem and allow us to incorporate new infrastructure into the model at a future date.
Based on Minimum Nakamoto coefficient.
Based on original Nakamoto Coefficient subsystems:
- Consensus nodes by client
- Consensus nodes by country
- Execution nodes by client
- Execution nodes by country
- Distribution of native asset by amount
- Amount staked by pool / staking service provider
Metrics pertaining to PBS:
- Blocks poposed by builder
- Blocks proposed by relay
Metrics pertaining to Account Abstraction:
- Number of user operations per bundler
- Number of wallets per deployer
Miscellaneous Metrics:
- Effective inflation rate adjusted for burn
- Percentage of total supply staked
- Layer 2 rollups by relative TVL
- Stablecoins by relative TVL
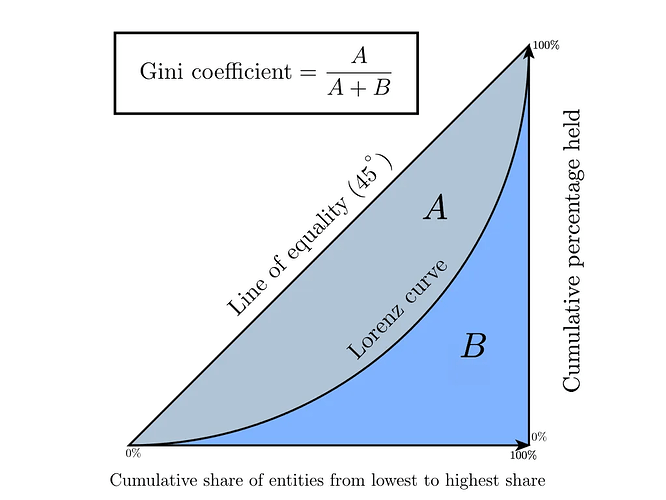
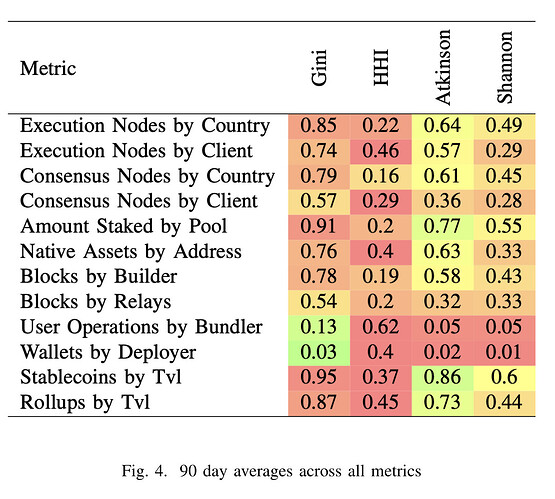
Deviations model: Gini index
Combinatorics model: Herfindahl-Hirschman index
Entropy model: Shannon index
Social welfare model: Atkinson index
Tail ratios: Palma ratio, Pareto ratio
Divergence measures: Jensen-Shannon Divergence
Weighted geometric mean: Master Index
Weights for master index:
Consensus nodes by client: 1
Consensus nodes by country: 1
Execution nodes by client: 1
Execution nodes by country: 1
Distribution of ETH by amount: 1
Amount staked by Pool: 1
Blocks proposed by builder: 0.7
Blocks proposed by relay: 0.7
Number of userops per bundler: 0.2
Number of wallets per deployer: 0.2
Layer 2 rollups by relative TVL: 0.5
Stablecoins by relative TVL: 0.3
Results
Decentralization is a dynamic quality that changes over time, rather than a static quality that is maintained in continuous equilibrium.
Different indices give divergent results when applied to the same data.
The master index establishes a measurement that can be referenced to itself as it changes over time.
Holistic view of the system.
Develop a way to measure potential collusion between entities within a population.